Finding the perfect adhesive that works with a wide range of materials, including cloth and plastic, is a never-ending search. Regardless of whether you are a DIY enthusiast, an art and crafts aficionado, or simply a restorer of a useful item for maintenance, it is essential to provide a high-performance, reliable bond between these materials. In the right hands, the right glue can result in some very professional-looking work, but in the wrong hands, the opposite can occur, meaning failed sections, a lot of precious labor, and a time-consuming dead end, are just a few examples. This is a simple look into the glues that have been developed to bond the cloth to the plastic, and we will find out how the glue is used, its practicality, and how easy it is to work with. This ranges from the know-how on adhesive formulae to tackling specific applications, and readers will have most of what they need to weigh different choices and complete the project.
Understanding Adhesives for Fabric to Plastic
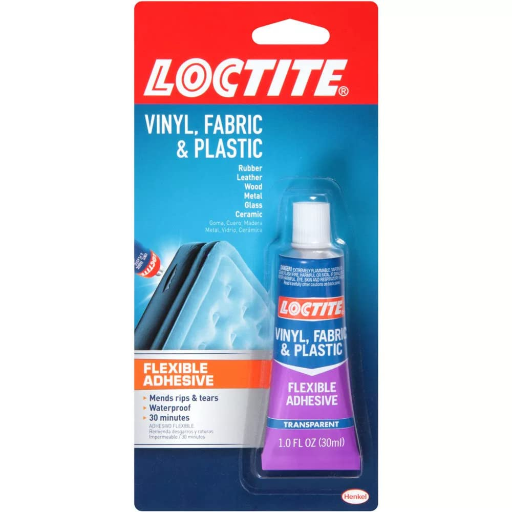

Understandably, great consideration needs to be given when acquiring adhesives that will glue fabrics to plastics because both are as opposed as they could get. Here is an overview of the appropriate adhesive types and their descriptions as alternatives to use with the thermoplastic and plastic materials:
- Epoxy Adhesives
Epoxy adhesives are known for their firm and effective bonds, this being why they are applicable in the connection of cloth to hard plastics. Epoxy glue is especially helpful in where there is expected wear and tear or loads are to be carried.
- Spray Adhesives
Spray adhesives are the most suitable for larger surface areas or light fabrics. With their widespread applicators helping even distribution, spray adhesives make them less problematic to use in unnecessary construction projects until their sticky has dried out.
- Hot Glue
Hot glue can be very convenient as it is a little more bendy and helpful to a certain extent, mainly used for making temporary, quick repairs. It is, however, not so recommended when the project requires high temperatures or long service life concepts.
- Cyanoacrylate (Super Glue)
Super glues are also ideal for covering small surfaces and substrates that have no pores. It creates a satisfactory bonding within the first few minutes, though it breaks, causes a systemic destruction of the bond or a loosening of the bond upon when subjected to repeated strain.
- Fabric-Specific Adhesives
All the above kinds are used with textiles, and permit some elongation if not full flexibility, that is, the bond is maintained even while the material is creased or bent away.
Key Features of Effective Adhesives
- Bond Strength
Adhesive bonding must sufficiently endure tensile, shear, and peel stress in the bonded area. For example, some of the epoxy adhesives can have tensile strength of up to 5000 psi, especially for duties in regimes of high strain like structural bonding.
- Curing Time
During normal application, the time taken for the adhesive to cure will determine just how effective the adhesive will be. Quick setting adhesives like cyanoacrylates might harden in seconds because of the presence of moisture in the atmosphere whereas it might take hours or even days for the two-part epoxies.
- Temperature Resistance
These adhesives should be able to withstand fluctuations in temperature. For instance, many high-temperature adhesives, such as silicones, can withstand steady temperature cycles up to 500°F, or endure extreme temperatures, down to -60°F without damage, and are therefore suitable for vertical or automotive bonding applications within the market.
- Flexibility
Certain situation types require that the bonding adhesives remain flexible after curing, and this is especially when bonding materials are susceptible to any form of movement or vibration. For its ability to accommodate joint movement and, at the same time, maintain high bond strength, polyurethane adhesives have constantly been popular.
- Chemical Resistance
Here, adhesives that are used must be resistant to exposure to harsh conditions such as oils, solvents, and acids. Epoxy and acrylic adhesives often provide outstanding chemical resistance, which makes them compatible with corrosive surroundings and enhances their service life.
- Viscosity
Benefits of Using the Right Glue
- Enhanced Bond Strength
The right adhesive helps boost the bond retention of the material over these areas. An illustration is that Structural Adhesives, like Epoxy, for instance, can have tensile shear strengths exceeding 3,000 psi. Ideal for accurate and heavy applications, especially in aerospace and automobile industries.
- Improved Durability
Assembling some pieces also demands the correct choice if a service is to be prolonged and the natural effect of the surroundings to be overruled. Even in an extreme environment, such as high temperatures and humidity, and, for instance, UV-curable adhesives, refrain electronic and optical components from deterioration, wear, and aging.
- Time and Cost Efficiency
When the right type of adhesive is used, there is a shortened curing time and hence production capabilities are bettered. So-called by an adjective that is hard to forget, Cyanoacrylate adhesives (“super glues”) will “disappear” at a quick time of around 10-60 seconds, and so will úť the need for additional staff and work processes in most production activities with busier production lines.
- Material Compatibility
Proper selection and application of adhesive prevents destruction of the substrate due to corrosion, warping and other issues. In particular, adhesives designed for plastics are known to work by releasing internal stress, which normally gives way to stress-induced cracking, and major polar or anti-stress components that interact with the material in any way.
- Environmental Resistance
There are distinct types of adhesives with respect to the contouring of the surface to be bonded, such as heat, moisture, or exposure to specific chemicals. Thus, for instance, the temperature-dependent range or resistance of silicone adhesives is quite impressive, ranging from -60°F to 500°F, and as such makes it a high-temperature adhesive.
- Weight Reduction
However, when compared with mechanical fasteners, the contribution of adhesives is seen in the structural applications where saving of weight is of paramount importance. Such advanced adhesive techniques that are used by aeronautical engineers improve fuel consumption, thus the overall performance of the aircraft.
- Aesthetic and Functional Advantages
They make a joint that is as strong as it is unnoticeable, which also means there are no mechanical fasteners, screws or welding beads spoiling the appearance of the product. Also, it ensures equal load on the adhesion on bonded parts which actually works with a distribution of tension over the bonded surfaces enhancing operational reliability of the structure in the final product design.
Top-Rated Glue Options

- Epoxy Adhesives
Epoxy adhesives are attractive owing to their outstanding adhesion ability and versatility; therefore, they are highly appreciated. They are a good fit for applying with different types of materials from metals to plastics or ceramics, so that in case there is a necessity, construction, automotive, or aerospace use is adequate. Most releases provide high protection against heat, chemicals, and harsh weather conditions, thus giving a long service life.
- Cyanoacrylate (Super Glue)
Cyanoacrylate adhesives are recognized for their fast setting time and ability to be used with ease. These glue the surfaces effectively without forming any bonds in the joint after separation, even if the surfaces are immiscible templates such as rubber, glass, and plastics. Even though not suitable for elastic materials, they are suitable when one needs literature repairs and small applications of delicate precision.
- Polyurethane Adhesives
Flexible and absorbent materials are also water-resistant and tough adhesives are preferred in this case to stick both materials and fix the porous network. They are flexible and can be applied to different materials such as wood, foam, or textiles. They are also resistant to moisture, hence they are suitable for both internal and external applications. Polyurethane adhesives are also used in furniture joints and the construction of floors.
- Silicone Adhesives
Gorilla Glue: Strength and Versatility
Gorilla Glue has become a sought-after brand due to its high-strength glue and potential for use in doing all kinds of things. The adhesive is designed to work on nearly all kinds of material, including wood, metal, stone, ceramic, and many other materials. Its specially designed polyurethane compound makes it resistant to both high and low temperatures and completely waterproof; it is suitable for different indoor and outdoor conditions, therefore even the most harsh climatic conditions will not affect its health or destroy the bond.
Also with Gorilla Glue, the adhesive solutions have the ability to greatly expand and shrink during curing, thus able to go inside porous materials and form a bond which remains for an extended period. However, proper use of such products must be observed as the adhesives may also expand, leading to excessive use. Moreover, its load-bearing ability makes it suitable for the heavy-duty maintenance of industrial or architectural structures. And while it offers great bond strength and adhesion to a wide range of materials, Gorilla Glue is unbeatable for demanding high-performance applications like those where a lot of flexibility is required.
Loctite Super Glue: Fast and Reliable
Loctite Super Glue is made suitable for use in quick adhesive spots by its built-in precision and quick bonding properties. The formula is made to stick as a bond permanently on applied materials, hence most materials within seconds are able to remain fastened together. The synergy prevents lengthy waiting times without in any way interfering with a strong permanent connection build up. It bonds various materials, including metals, and has a fairly wide bond space, especially for metals. Loctite Super Glue also provides high-level resistance against smash impact as well as the surrounding environment, for example, humidity and also alterations in temperature, hence it can still be used under challenging conditions. As well, the precision tips for directing and controlled flow system design have made it easy to use, and have helped reduce mess and enhance accuracy in application.
3M Super 77: All-Purpose Adhesive
No need to say more than the fact that 3M Super 77 Spray Adhesive is a very versatile product that can bond many lightweight substrates effectively and efficiently. This results from its fast tack and high coverage characteristics in which makes the adhesive effective in sticking materials such as paper, cardboard, cloth and foam insulation among others. It is especially appreciated in the arts, crafts, and buildings sectors as it is both quick to use and performs consistently well. 3M Super 77, on the other hand, is designed to bond permanently for a long period, while at its initial stages, it is still relocateable, thus reducing offset and improving accuracy. It also guards against smearing as it does not penetrate materials too deeply to the point of damaging them. The adhesive is certified according to numerous safety and environmental regulations thus a useful and sustainable choice in several artistic and professional spheres.
Application Methods for Bonding Fabric and Plastic
- Surface Preparation
Ensure before and after bonding surfaces that have been in contact with other elements such as moisture. Handling hands with a mild detergent or rubbing alcohol should help in wiping areas free of grease that might ruin adhesion.
- Adhesive Application
All surfaces with inadequate adhesive bonds should have an appropriate coat of adhesive upon them, following the appropriate application guide. Spray adhesives are most effective for large applications, while liquids or gels are for use in minute joints.
- Positioning and Bonding
The materials are to be precisely placed and joined to the plastic or fabric. Make certain that no alterations are made before the adhesive bond is created. Apply no more than reasonable even pressure across the bonded areas to lock the contact.
- Curing Time
It is very necessary to allow the adhesive to dry or cure for the stipulated period as per the adhesive manufacturer. Command and confirm the demographic settings.
- Finishing Touches
Preparing Surfaces for Adhesion
For optimal adhesion and bond service life, surface preparation is compulsory. The substrate needs to be cleaned, giving attention to the removal of particulate materials such as dirt, grease, oil, or dust, among many other adhesive performance killers. This is because the structures commonly employed have wet cleaning techniques using solvents, like isopropyl alcohol or acetone, and they disintegrate debris. Most importantly, the substrate should be well dried to prevent water penetration before finally applying the adhesive.
The adhesion, in turn, is closely associated with the nature or state of the exposed surface. For instance, there are cases where the smooth surfaces often demand some form of abrasion in order to create a micro-textured finish and hence an increase in surface area for bonding. Methods, including sanding and grit blasting, serve the purpose. Moreover, the use of a suitable primer on the substrate can provide better adhesion capability by slightly changing the surface treatment on the interface.
It is essential to prevent any influence to the adhesive by maintaining specific environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, during surface preparation that are in accordance with the recommendations of the adhesive. Unfavorable circumstances can result in a drop in the adhesive’s functionality and can decrease both the adhesive and the performance. By following best practices during the preparation of surfaces, perfect adhesion is achieved for better performance due to the particular use of these adhesives.
Tips for Achieving a Strong Bond
- Surface Cleanliness
Within the cement paste wetting process, pollutants such as dirt, grease and oil will profoundly affect wetting and hence the bond strength. Case studies indicate that even the tiniest amount of residual material may lower the strength of bonding by up to 60%, a damaging level. To this end, corner areas are invariably cleaned with IPA (isopropyl alcohol) or two-part adhesive-characterized solvents in order to ensure even greater cleanliness.
- Surface Roughness
Mechanical interlocking of surfaces is achieved through the roughening of surfaces. For roughened surfaces, it is recommended to achieve a profile ranging from 40 to 60 microns (μm) as required. To ensure the required level of roughness, the surface should be inspected preferably cell-wise on profilometry or on sandblasting in compliance with the materials in use sheet.
- Priming the Surface
Regarding the adhesive, it is essential to note that applying a primer compatible with both the adhesive and the workpiece facilitates the establishment of a chemical bond. For one type of adhesive, it was found that using primers resulted in as much as 30% higher adhesion (strength). The permissible delay depends on the type of adhesive and the measurements of the primer specified in the adhesive data sheet (s).
- Controlled Application Environment
Subject surfaces to the temperature and humidity during the job, consistent with the values prescribed by the adhesive manufacturer, e.g., 65°F to 85°F and 40% to 60% relative humidity. Studies have shown that not following these guidelines can cause a decrease in the adhesive properties by 15%-20%. Environmental monitoring tools that are calibrated should be used to facilitate checking.
- Adhesive Mixing Accuracy
In the case of two-part adhesives, wrong resin-to-hardener mixture ratios have a significant effect on the speed of healing and physical structure of the bond. The mixture must correspond to the indicated (for example, 1:1 or 2:1, by weight or volume). For carrying out this procedure, it is recommended to use systems for dispensing with accuracy.
- Application Thickness
Comparative Analysis of Adhesives

Mechanical strength, material compatibility, and resistance to environmental factors are also important forces to take into account when it is necessary to make a comparison with respect to the given adhesives. Epoxy adhesives, for example, are known to be very strong in shear and tough; hence, they are mainly used as strong structural adhesives. Cyanoacrylate glues give the advantage of instantaneous bonding; however, they fail under load-bearing conditions at high temperatures. For those areas, polyurethane adhesives are flexible and enhance good bond strength, especially against such surfaces requiring impact.
Silicone adhesives, on the other hand, are advantageous when it comes to temperature changes and moisture since they are effectively non-responsive in the presence of moisture. They are thereby appropriate for sealing and bonding in adverse conditions. Yet these adhesives do not perform well in terms of mechanical strength compared to other adhesive types. To solve such a problem, the chosen adhesive will have to be one that meets the following considerations, including the useful field application factors and substance materials, as well as the adverse climatic factors.
Pros and Cons of Each Glue Type
|
Glue Type |
Pros |
Cons |
|---|---|---|
|
Epoxy |
High strength and durability |
Requires precise mixing and curing |
|
Super Glue |
Rapid bonding; easy to use |
Limited gap-filling capability |
|
Hot Melt Adhesive |
Quick setting; cost-effective |
Weak in high-temperature conditions |
|
Silicone Adhesive |
Excellent temperature and moisture resistance |
Lower mechanical strength |
|
Polyurethane Glue |
Strong bond; versatile on materials |
Long curing time; requires moisture |
|
Acrylic Adhesive |
High impact resistance; weatherproof |
Higher cost than other adhesives |
|
PVA (Wood Glue) |
Non-toxic and easy to clean |
Limited water resistance without seal |
|
Contact Cement |
Instant bonding for large surfaces |
Emits strong fumes during application |
|
UV Cure Adhesive |
Cures under UV light; precise bonding |
Requires specialized equipment |
|
Anaerobic Adhesives |
Ideal for metal and thread-locking |
Limited use on non-metal materials |
Comparison Chart of Best Adhesives
|
Adhesive Type |
Key Advantages |
Key Limitations |
Recommended Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Epoxy Resin |
High strength; durable |
Long curing time |
Metal, ceramics, wood bonding |
|
Cyanoacrylate (Super Glue) |
Fast cure; strong bond |
Brittle under stress |
Small repairs, non-flexible materials |
|
Polyurethane Adhesive |
Strong; flexible; waterproof |
Difficult to remove |
Wood, glass, outdoor projects |
|
Silicone Sealant |
Waterproof; heat resistant |
Limited structural strength |
Gaps, sealing joints |
|
Hot Melt Adhesive |
Quick setting; easy application |
Less strong in high heat |
Crafts, packaging, temporary bonds |
|
Acrylic Adhesive |
High impact resistance; weatherproof |
Higher cost than others |
Structural assemblies, outdoor bonds |
|
PVA (Wood Glue) |
Non-toxic; easy cleanup |
Limited water resistance without seal |
Wooden furniture, carpentry |
|
Contact Cement |
Instant bonding; large areas |
Strong fumes during application |
Flooring, laminates, large surfaces |
|
UV Cure Adhesive |
Precise bonding; quick under UV |
Needs specialized equipment |
Electronics, glass-to-glass bonding |
|
Anaerobic Adhesive |
Ideal for metal; thread-locking |
Limited use on non-metal materials |
Automotive, machinery |
|
Polyvinyl Acetate |
Versatile; non-toxic |
Low water resistance |
Paper, light wood |
|
Rubber Cement |
Flexible; peelable |
Weak bond over time |
Photos, temporary crafts |
|
Phenolic Resin |
Heat resistant; chemical resistant |
Brittleness under mechanical loads |
Industrial brakes, adhesives |
|
Spray Adhesive |
Easy to apply; even coverage |
Not suitable for heavy-duty uses |
Lightweight materials, fabrics |
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them

- Using the Wrong Adhesive for the Material
Picking an incompatible glue can be problematic because the bond can fail. Using rubber cement on a bulk material, for instance, would be a very poor idea, and the joining strength would definitely be insufficient.
Solution: Cross-check the requirements of the adhesive, in particular in relation to the materials used.
- Ignoring Surface Preparation
The bonding of two pieces of materials may also be degraded by pollution or contaminants, e.g., dirt, dust, grease, etc.
Solution: For effective bonding, remove dirt from surfaces and let them air out first before application of any adhesive.
- Applying Insufficient or Excessive Adhesive
The adhesive bonds may not form well if not enough glue is applied, and if glue is applied in excess, the result could be uneven curing or a mess.
Solution: Use the recommended adhesive amount as per the application instructions prescribed by the manufacturer.
- Exposing Adhesives to Improper Environmental Conditions
Some adhesives degrade when exposed to extreme temperatures, for instance, high or low temperatures, as well as moisture conditions. For example, Polyvinyl Acetate, when exposed to wet places, never gives its expected results.
Solution: Ensure that the adhesive is compatible with the environmental conditions of operation.
- Failing to Allow Proper Curing Time
The bond could be compromised if substandard results are achieved and the adhesive does not cure properly before the new part is made.
Solution: Please ensure that the amount of time you have to wait until the adhesive cures until it is used is adhered to.
Preparing Surfaces Incorrectly
When the surfaces where the adhesive will be applied are not prepared correctly, there may be a big decline in the performance of the adhesive joint, which will in turn fail sooner than expected. For example, one of the reasons could be due to poor cleaning, which might result in the presence of oil, dust, or grease on the surface, which would hinder the adhesion properties. Besides, the form of the surface also matters; a very smooth and polished surface may cause the failure of the adhesive to hold on properly. Research shows that recent improvements in materials technology have made it possible to enhance bond strength by up to forty percent through the physical preparation of the bonding surface by scuffing or drawing the rough surface, thereby increasing mechanical interlocking. Cleaning agents or degreasers should be used for pre-application surface treatment. If any residues remain, they must be completely cleaned, and only then should the adhesive be applied to the surface. A primer can be applied on metal surfaces to improve further adhesion as well as provide resistance to environmental conditions.
Not Allowing Adequate Drying Time
It has been found that not allowing enough time for adhesive drying prior to going to the next step in bonding practice can be detrimental to the success of the bond. The investigation recognized that a lack of drying can retain solvents or moisture in the adhesive layer, which may later cause low adhesion or even bond breakdown under load. Several factors, such as adhesive type, nature of the substrate, room temperature, and RH, determine the time it takes for an adhesive to dry. Epoxies, for instance, may need several hours to build up time and expose to given temperatures for maximum efficiency as stated under technical data prepared and offered by the manufacturer. One must adhere to the recommended drying times to fully benefit from the adhesive and achieve reasonable levels of its mechanical properties and chemical resistance.
Using Incompatible Adhesives
Reference Sources
-
Loctite Consumer: Gluing Fabric to Plastic
This guide emphasizes the importance of selecting the right adhesive for bonding fabric to plastic. It highlights three main types of adhesives: fabric glue, contact adhesive, and spray adhesive. Each type is suited for different applications, with spray adhesive being ideal for delicate materials and larger areas. -
UniBond: Gluing Fabric to Plastic – Useful Techniques
This guide focuses on selecting the right adhesive for fabric-to-plastic bonding, recommending flexible, specially formulated glues. It outlines techniques for general bonding and repairing rips or tears, emphasizing surface preparation, applying glue evenly, and using patches for larger repairs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the best glue for fabric to plastic?
A: The best glue for fabric to plastic often depends on the specific materials you’re working with. For a strong bond, consider using fabric adhesives like Aleene’s or Gorilla glue, which are designed to create a permanent bond between these two surfaces. Both options dry clear, making them ideal for projects where aesthetics matter. Always ensure the materials are clean and dry before applying the adhesive. It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the best results, which typically recommend applying a small amount of glue to both surfaces and pressing them together until the glue sets.
Q: How do I attach fabric to plastic?
A: Attaching fabric to plastic can be done effectively using specific types of glue. A flexible adhesive or a contact cement is often a good choice, as they allow for some movement without compromising the bond. To start, clean both surfaces thoroughly and apply a small amount of glue. Press the edges together and hold until the glue dries. Using masking tape around the edges can help keep them in place while the adhesive cures. For quick repairs, super glue can also be effective but may not provide the same flexibility as fabric-specific adhesives.
Q: Can I use super glue for fabric and plastic?
A: While super glue can bond fabric to plastic, it may not be the best choice for projects that require flexibility. Super glue dries very quickly and forms a strong bond but can make the fabric stiff. If your project involves frequent movement, consider using a fabric glue that is specially formulated for this purpose. These adhesives not only bond well but also allow the fabric to remain flexible, which is essential for wearables or items that will be handled frequently. Always test on a small area first to ensure compatibility.
Q: What type of adhesive is best for quick repairs?
A: For quick repairs, an all-purpose adhesive or a spray adhesive like 3M Super 77 can be very effective. These types of glue provide a fast bond and are easy to apply. Make sure to work in a well-ventilated area and apply a small amount of glue to both surfaces for the best results. If you’re working on crafts, using a fabric glue that dries clear is beneficial for maintaining a neat appearance. For heavier fabrics, consider using an extra strong adhesive that can handle the weight without sagging.
Q: How can I ensure my fabric and plastic bond remains strong?
A: To ensure a strong bond between fabric and plastic, start by using the right adhesive. Look for fabric adhesives specifically designed for this purpose, as they provide a permanent bond while allowing flexibility. Prepare your surfaces by making sure they are clean and dry before applying the glue. A good technique is to apply the glue to both surfaces and press them together, holding them until the glue sets. Additionally, if you’re working with larger pieces, consider using masking tape to secure the edges while drying. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines on drying times will also help achieve the best outcome.



















