When it comes to plastic repair or bonding, choosing the right adhesive can be one of the most tedious and confusing tasks. The fact is that not all glues are the same in terms of effectiveness, and if you accidentally choose the wrong one, you could end up with poor results or even further damage to your project. This is the point at which epoxy glue for plastic emerges as a game-changer. Resilient, mixed-use, and easy to work with, epoxy adhesives have been the go-to solution for both minor home repairs and the most challenging industrial work.
The guide below provides everything you need to know about using epoxy glue for plastic: how it works, its advantages, and how to use it effectively. As a matter of fact, whether you are a DIY enthusiast or a professional seeking dependable bonding options, this thorough resource is your best bet. The revelations of strong, enduring repairs and bonds made with epoxy are soon to be unveiled to you!
Understanding Epoxy Adhesives
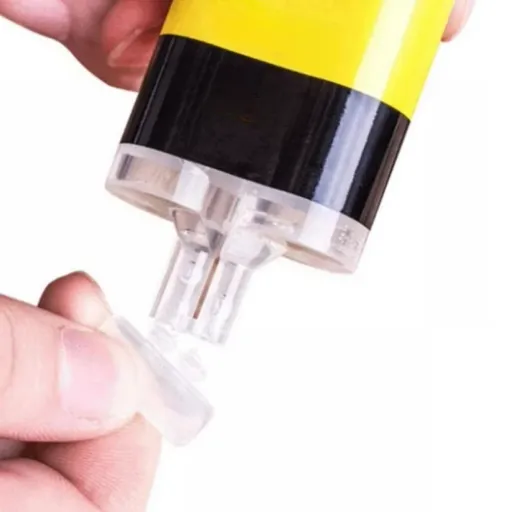
Epoxy adhesives are bonding agents that consist of two parts, a resin and a hardener. These two components, once mixed, undergo a chemical reaction that forms a strong, durable bond. Such adhesives are super flexible and can stick to a wide range of materials like plastic, metal, wood, and glass. Besides being heat-, water-, and chemical-resistant, epoxy adhesives are widely used for their strength in repairs, construction, and manufacturing. Their effectiveness depends on proper surface preparation, correct mixing, and sufficient curing time, making them a dependable option for both household and professional use.
What is Epoxy Glue?
Epoxy glue is an adhesive of the highest performance that uses a chemical reaction, or curing, to form a strong, durable bond. Curing generally occurs when two components, a resin and a hardener, are mixed. This amazing adhesive has a wide range of uses and is renowned for bonding a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, wood, and glass.
Epoxy glue’s properties, including heat, water, and chemical resistance, make it a go-to option across industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, construction, and crafting. It is especially appreciated for making long-lasting seals and repairs. The latest innovations in epoxy glue formulas have made them cure more quickly, be more flexible, and even more environmentally friendly, positioning them not only as a reliable but also an innovative choice for a range of applications, from home projects to industrial manufacturing.
The Science Behind Epoxy Resin
Epoxy resin is a two-part mix, with one part epoxy resin and the other a curing agent—commonly called a hardener. The mixing of these two components initiates a chemical reaction, known as polymerization, that converts the liquid resin into a solid thermoset. The reaction is exothermic because the two components bond at the molecular level, forming a rigid, durable crosslinked structure.
Key Performance Characteristics
One trait of epoxy resin that many people find most captivating is its ability to perform multiple roles—the very aspect that makes it so popular. Manufacturers can tailor the resin’s properties to their preferences by adjusting the formulation; thus, curing time, softness, and heat resistance can be customized.
- Tensile Strength: Studies suggest that epoxy resins can achieve tensile strengths of up to 60 MPa (Megapascals), making them robust materials for construction and industrial applications.
- Bond Strength: The strong bond of epoxy adhesive can reach 30 MPa, significantly higher than the strength of many regular glues.
- Environmental Innovation: Recent developments focus on eco-friendliness through bio-based formulations that use renewable raw materials, reducing petroleum-based inputs.
Types of Epoxy for Plastic Bonding
General-Purpose Epoxy
General-purpose epoxy is the most common adhesive for plastics because it is suitable for all types. It features high adhesion and long-lasting durability, making it very versatile and ideal for light repairs and household applications.
Plastic-Specific Epoxy
Plastic-specific epoxies are designed to bond with common plastics such as polypropylene, polyethylene, and PVC. In most cases, they will contain boosters or special forms to provide better adhesion.
Fast-Setting Epoxy
Fast-setting epoxy is perfect for rapid fixes, as it hardens very quickly — sometimes in a matter of minutes — and still provides strong bonding power.
High-Strength Epoxy
High-strength epoxy is intended for heavy-duty situations and it gives the strongest bond among all types of epoxies. It is also excellent in tolerating changes in temperature and environmental influences.
Flexible Epoxy
Flexible formulations are very significant for plastics that constantly bend or move. The epoxy will remain intact and strong, without becoming brittle or breaking under pressure.
⚠️ Important Note: Different types of epoxy have their own specific application guidelines, so the correct one should be picked depending on the type of plastic and its use. Always adhere to the manufacturer’s directions to ensure the best results.
How Epoxy Glue Works on Plastic

Plastic surfaces are joined with epoxy glue through a chemical reaction between a hardener and a resin binder, producing a robust, enduring bond. When these two chemical components are blended, they cure to form a tough, high-strength bonding layer that goes into the plastic’s surface. Surface treatment is the most critical factor; the plastic is made perfect for adhesion through not only cleaning but also applying fine sanding.
The adhesive can withstand stresses, temperature changes, and humidity after complete curing because it is designed to bridge gaps. Consequently, epoxy glue is a dependable option for plastic repair and bonding of different kinds. For best results, always check the specific plastic type compatibility.
The Mechanism of Adhesion
The adhesion of epoxy glue depends on a chemical reaction called polymerization. Generally, epoxy resins have two main components—resin and hardener—that when mixed together, take part in a curing process which results in a robust, long-lasting adhesive bond. The adhesive interacts with the material’s surface at the microscopic level, thus establishing a physical interlock.
In addition, glue and substrate interact chemically through forces such as van der Waals interactions and covalent bonding, which provide a strong bond. For plastics, surface preparation enhances this bond by increasing contact and removing unwanted materials. Today’s formulations, as noted in recent studies, use additives to improve adhesion to low-energy surfaces such as polypropylene and polyethylene, thereby overcoming bonding problems with these materials. So, the mechanism of epoxy glue combines surface interaction with chemical bonding to impart strength, resilience, and versatility across many other applications.
Factors Influencing Bond Strength
- Surface Roughness:
A rougher surface provides the adhesive with more area to bond, thereby improving overall bonding strength and mechanical interlocking.
- Surface Cleanliness:
The adhesion process is more efficient when contaminants such as dust, oil, or grease are absent, as these substances do not impede glue contact.
- Adhesive Type:
Bond strength is highly influenced by the adhesive’s chemical composition and its properties relative to the materials.
- Application Method:
The use of proper application methods, such as uniform spreading or maintaining the correct thickness, helps the bond last longer.
- Environmental Conditions:
Curing process and adhesive’s performance over time can be influenced by temperature, humidity, and chemicals as environmental factors.
Comparing Epoxy to Other Adhesives
| Parameter | Epoxy | Cyanoacrylate | Polyurethane | Silicone | Acrylic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | High | Moderate | Moderate | Low | High |
| Durability | Excellent | Low | Good | Good | Good |
| Flexibility | Low | Low | High | High | Moderate |
| Temperature Resistance | High | Low | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Cure Time | Long | Short | Moderate | Long | Short |
| Bond Types | Variety | Limited | Variety | Flexible | Rigid |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent | Low | High | High | Moderate |
| Cost | Moderate | Low | Moderate | High | Moderate |
This table provides a concise comparison of key parameters for selecting the appropriate adhesive based on application needs.
Best Practices for Using Epoxy on Plastic

- Surface Preparation:
The plastic surface should be cleaned thoroughly to remove dirt, grease, and other contaminants. Better adhesion can be achieved by lightly roughening the area with sandpaper.
- Choose the Right Epoxy:
Always check whether the epoxy is compatible with the type of plastic being bonded. The best result may require a specific formulation or primer for some plastics.
- Mix Properly:
The mixing of resin and hardener should be done as per the manufacturer’s instructions to achieve a strong bond.
- Apply Evenly:
An applicator should be used to spread the epoxy uniformly over the surface, avoiding bubbles or gaps.
- Allow Sufficient Cure Time:
The epoxy should be given enough time to cure in accordance with the recommended period and conditions like temperature and humidity.
- Safety Measures:
Work in a well-ventilated area and wear gloves to protect your skin, as the epoxy is skin-sensitive.
💡 Pro Tip: When you adhere to these best practices, your epoxy plastic bonding will be both strong and long-lasting.
Preparation Techniques for Plastic Surfaces
Step 1: Clean the Surface Thoroughly
A mild detergent mixed with water is the best way to clean the area of dirt, grease, and other contaminants. After that, dry the surface thoroughly before proceeding.
Step 2: Roughen the Surface
Lightly sand the plastic with fine-grit sandpaper (e.g., 220-300 grit) to improve adhesion.
Step 3: Wipe Down with Isopropyl Alcohol
After sanding, clean the area with isopropyl alcohol to remove any remaining dust and oils.
Step 4: Testing for Compatibility
To ensure a good bond with the material, apply a little epoxy in an area that is hard to see.
With proper surface preparation on the plastic, you can expect a strong bond, and the process will not need to be repeated for a long time.
Step-by-Step Guide to Mixing Epoxy
Instructions Reading
The first step is to read the manufacturer’s instructions for the epoxy resin and hardener very carefully. There may be some unique mixing ratios or guidelines for each product.
Components Measuring
Use very accurate measuring instruments to ensure the resin-to-hardener ratio is correct as specified in the instructions. Wrong ratios can either weaken the bond or prolong the curing process.
Mixing Container Selection
Use a clean, disposable mixing container to avoid contamination. It should be the right size for the amount of epoxy you plan to mix.
Resin and Hardener Combination
The mixing container will receive the measured resin and hardener. Care should be taken to scrape out the entire contents of each measuring tool to ensure the correct ratio is maintained.
Mixing Thoroughly
A clean mixing stick or paddle will do the stirring of the resin and hardener together. Stirring should be slow and steady to avoid air bubbles in the mixture, and frequent scraping of the container’s sides and bottom is essential.
Mixing Time Observing
Follow the manufacturer’s recommended mixing time to ensure the resin and hardener are thoroughly blended. This step is critical in getting the best results during application.
Uniformity Checking
As soon as the mixture is complete, the epoxy will need to have a smooth, even texture and color, with no streaks or undissolved particles. Keep stirring until it is all of one color if there are any streaks.
✓ Success Tip: If you strictly adhere to these steps, you will be able to get a perfectly blended epoxy that is suitable for any usage and provides a strong and durable bond.
Applying Epoxy Glue Effectively
I do the cleaning process first when applying epoxy glue, which means I start with spotless and dry surfaces, along with the removal of grease or dirt if any. A disposable applicator or tool is then utilized for the even spreading of the epoxy over the surface with full coverage being the main aim. After that, I really push the two surfaces together and hold them until the glue sets. I always respect the manufacturer’s instructions and let the adhesive cure completely for the best bond.
Drying and Curing Times

The drying and curing times of plastic epoxy glue can vary depending on the product and surrounding conditions. Usually, most epoxy glues take about 30 minutes to reach the setting stage, but complete cure may take 24 to 72 hours. Adhering to the manufacturer’s instructions is paramount, as some adhesives may require additional curing time to reach maximum strength, especially on non-porous surfaces such as plastic.
Understanding Drying Time vs. Curing Time
Drying time refers to the initial setting period during which the epoxy hardens enough to be handled, while curing time is the more extended period required for the epoxy to reach its maximum strength and durability.
| Parameter | Definition | Duration | Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drying Time | Initial set | ~30 mins | Room temp |
| Curing Time | Full strength | 24-72 hours | Environmental |
| Affects | Handleability | Short-term use | No pressure |
| Use Readiness | Structural use | After curing | Full cure |
Factors Affecting Curing Times
- ●
Temperature – The curing process is generally quicker at higher temperatures and slower at lower temperatures. - ●
Humidity Levels – A humid environment can delay the curing process due to moisture in the air. - ●
Type of Glue – The curing times and requirements of adhesives are determined by their chemical compositions which vary for different types of glues. - ●
Plastic Material – The curing time is determined by the type of plastic being glued, since some plastics have non-sticky surfaces that require longer curing time. - ●
Thickness of Application – A thick application of glue will take longer to cure than a thin one.
Tips for Faster Curing
Ensure Proper Ventilation
Good ventilation should be a prerequisite for the work area, since it not only facilitates evaporation and curing but also speeds them up.
Apply Heat
Lightly warm up the glued area with a low-temperature heat source (like a hairdryer or heat gun) and hasten curing (just make sure the plastic can handle the heat).
Use a Thin Layer
Applying glue in a thin, even layer not only ensures proper bonding but also allows for quicker curing than a thicker application.
Choose a Fast-Curing Adhesive
Specialty glues intended for rapid curing, such as cyanoacrylate or other quick-bond adhesives, are the ones you should go for.
Prepare the Surface
Plastic surfaces should be sanded or cleaned to remove grease and debris, thereby improving adhesion and enabling faster curing.
Common Plastic Types and Epoxy Compatibility

Different types of plastic exhibit varying degrees of compatibility with epoxy adhesives. The following is a summary of the most popular plastic kinds and the corresponding epoxy compatibility:
⚠️ Polyethylene (PE) and Polypropylene (PP)
They are considered the low-surface-energy plastics, and it is tough to use epoxy on them. They can be treated with flame beforehand, but it still does not guarantee a powerful bond.
Polycarbonate (PC)
After thoroughly cleaning the surface, epoxy adheres well to polycarbonate. Do not apply too much heat during curing, as it may cause the plastic to deform.
✓ Acrylic (PMMA)
If the acrylic surfaces are cleaned and sanded correctly, epoxy usually bonds very well to them.
✓ ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
ABS is compatible with most epoxy adhesives, particularly when the surface is sanded to improve bond strength.
✓ PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Epoxy performs well on PVC when the surfaces are cleaned and slightly roughened before application.
⚠️ Critical Reminder: Surface preparation is a key factor no matter what type of plastic you are working with. Cleaning, sanding, and choosing the appropriate epoxy are essential for creating a bond that will last.
Which Plastics Bond Well with Epoxy?
Epoxy is a perfect adhesive for some plastics, especially when the surface is prepared correctly. The following types of plastics are o.k with epoxy:
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene – Epoxy sticks well to ABS, but the surface should be sanded and cleaned to improve adhesion.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is very compatible with epoxy, but the surface should be cleaned, lightly roughened, and kept free of contaminants.
If proper preparation is done like light sanding and degreasing, polycarbonate will form a powerful bond with epoxy.
Cleaning and sanding the plastic surface before applying epoxy will provide the strongest, longest-lasting bond.
How to Test Plastic Compatibility
Testing for epoxy compatibility with plastic can be done by carrying out the following activities:
Step 1: Test Area Preparation
Determine a minor area that is not readily visible in the plastic material to conduct the test. This will make it possible that any damage done or the failure of the material during the test will not affect the larger piece.
Step 2: Cleaning the Surfaces
Using isopropyl alcohol or a mild detergent, clean the plastic surface and remove any dust, grease, or other contaminants. Then, let it dry completely.
Step 3: Test Area Light Sanding
With fine-grit sandpaper (like 220-grit), smooth the surface very slightly. This will provide the surface texture that is necessary for good adhesion of the epoxy.
Step 4: Mixing and Applying Epoxy
In accordance with the manufacturer’s directions, prepare a small quantity of epoxy, and then apply it into the prepared test area.
Step 5: Epoxy Curing
The epoxy should be allowed to cure according to the manufacturer’s directions for curing time.
Step 6: Bond Strength Test
Test the bond by applying pressure to the area that was glued after curing. Decide on the basis of whether there was a strong bond between epoxy and plastic or not depending on the absence or presence of peeling or cracking.
💡 Key Insight: You will be able to find out that your plastic material is compatible with epoxy and also that surface preparation needs to be adjusted to get the best results by simply following these steps.
Special Considerations for Different Plastic Surfaces
🔸 Polyethylene and Polypropylene
These plastics have slick and smooth surfaces that are non-porous which means they are resistant to bonding naturally. If you want better adhesion, you can use a plastic adhesive primer or lightly sand the surface to create texture before applying the epoxy.
🔸 PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
PVC is one of the plastics that epoxy bonds best with, but first, make sure that the surface is clean and there are no grease or oils. Using a degreaser or isopropyl alcohol before applying epoxy can improve the outcome.
🔸 Acrylic and Polycarbonate
These types of plastics are likely to get scratched and damaged. Do not over-sand; instead, make sure the surface is spotless, with no dust or debris, before applying the epoxy.
🔸 ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
ABS is a type of plastic that usually adheres well to epoxy. For the best results, first clean and lightly sand the surface, then let it dry before application.
By taking these requirements into account, you can achieve optimal adhesion to various plastic surfaces.
Reference Sources
- An Investigation and Research Regarding the Adhesive Qualities of Epoxy Resins in Architectural Construction
This study discusses the adhesive properties of epoxy resins and their applications.
- Mimicking Nature to Design Degradable Adhesives from Renewable Resources
This thesis explores various adhesive types, including epoxy, and their bonding capabilities with plastics.
- An-Najah National University Repository: Production and Characterization of Marble Glue
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
❓ What is plastic epoxy adhesive?
Plastic epoxy adhesive is a two-part glue made of resin and hardener that requires mixing the parts to achieve the strongest bond; hence, it is the first choice for restoring broken plastic items. Its water resistance, toughness, and ability to stick to even very different types of plastic make this glue highly applicable for both indoor and outdoor use.
❓ How does the drying time of epoxy glue affect its use?
Drying times for epoxy glues vary widely, but products giving up to 5-minute epoxy, offering a rapid setting time for fast repairs, are among the most commonly used. Proper curing of the bond is essential for achieving the strongest possible epoxy adhesion; thus, it is recommended to follow the manufacturer’s curing time and conditions for best results.
❓ What types of plastics can be bonded with epoxy glue?
Epoxy glue for plastic is not only versatile but also applicable to a wide range of plastics, including PVC, ABS, and polycarbonate. The only thing that is important to keep in mind is that the application of the adhesive should follow thorough cleaning and proper drying of the surfaces for best bonding and also durability.
❓ Is epoxy adhesive water resistant?
The answer is affirmative, as many epoxy adhesives are water-resistant, making them suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications. This waterproof property is a significant factor in making the bond strong and long-lasting, making it ideal for repairs prone to wetness and able to endure various weather conditions.
❓ How will a syringe help in doing epoxy glue application?
Using a syringe for applying epoxy glue is very advantageous as it allows for precise application especially when the application point is small or when working on tiny plastic pieces. Just fill the syringe with the mixed hardener and resin, then gently spread it over the surfaces to be bonded, ensuring uniform distribution for the best results.
❓ Can the use of epoxy glues be extended to plastic welding?
Not exactly as epoxy glue is not a plastic welding method. However, it can still bond plastic parts, as in a welding process. The physical and chemical changes that occur during the mixing of the epoxy resin and hardener result in a bond that resembles welds in terms of strength and durability, particularly when restoring broken plastic items.
❓ Is there a food-safe epoxy glue for plastic?
Pointing to the fact that certain epoxy glues are made to be food safe, the answer is Yes. Anyone who is looking to use such a product where the bonded objects might be handling food, will not be disappointed since the glue does not have any harmful chemicals. Always look for safety certificates in product descriptions if you are considering using epoxy in the food industry.



















