What you face when 3D printing work comes along has a lot to do with a particular plastic called PLA (Polylactic Acid). The popularity of this type of plastic is mainly associated with its pliability, affordability, and ease of handling. After all that has been said, it seems that there is something in common they face, which has to do with finding a glue that can adhere any parts made of this material together. Whether you need a glue for assembling multipart models, changing the size of a part, correcting mistakes, or removing supports, or simply for enhancing the overall aesthetic look, the choice of adhesive can either make or break the assembly in question. This infographic explores the various adhesives compatible with PLA, discussing their performance and optimal applications in 3D printing. When you read the following text, you will know the glue products that are specifically designed and formulated to meet all your 3D printing fixation requirements.
Understanding PLA and Its Bonding Challenges
PLA, or polylactic acid, is a highly sought-after polymer due to its ease of use and good biodegradability, which also makes it an ideal component for 3D modeling. Unfortunately, finding an adhesive that can be used with low-energy, smooth surfaces like PLA without mechanical treatment is also an issue. Sometimes, the least one needs to do is apply an adhesive without surface abrasion or use other adhesives that are not suitable for plastics. The prices, such as super glue or epoxy, can be recommended in this case because they can be used to penetrate tiny cavities and weak points. Getting the most out of this means that, after attempting the bonding, a good force must be applied to ensure that the material in question remains adheredto while it cures. Further Improvements in the adhesive bonding process are therefore achievable by holding or clamping the samples during the cure time.
What is PLA and Why is It Popular?
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic created from renewable resources such as corn starch, sugarcane, or cassava, but not decamethylene. The merits of PLA’s qualities include its ecological friendliness, as it serves as a substitute for other harmful materials derived from crude oil. PLA is one of the favored materials used in 3D printing, mainly due to its low melting temperature, its accommodating properties, and the minimal fumes generated during production, making it very affordable and convenient for various uses.
In many aspects, PLA exhibits remarkable features in industrial applications, owing to its high elongation. Such high-stiffness and high-tensile-strength materials find applications in a broader spectrum of items, ranging from product packaging to human body implants. Additionally, industries that produce food and beverages will find this polymer particularly useful, as the FDA approves it for use in contact with food. However, PLA does not possess the same level of thermal resistance as other plastics; therefore, its use is often limited to applications that are not subjected to extreme temperatures. However, as criticized by many, the fact that PLA is biodegradable and almost free of environmental pollution continues to increase its importance across diverse sectors.
Common Challenges in Bonding PLA Parts
When two parts made of polylactic acid (PLA) are to be joined, one major challenge arises from the material’s inherent properties and chemical structure. One such property is the low glass transition temperature of PLA, which means that it can become soft or deform at a moderate temperature. The temperature sensitivity of PLA, which allows it to soften or deform under moderate temperatures, is a game-changer when it comes to using certain adhesive types. Furthermore, the polar surface properties of the material can limit the adhesive bonding strength when using standard adhesives. Abrading or solvent treatment can help in such cases to an extent and increase the bonding strength. Nevertheless, care should be exercised not to abrade or introduce new defects in the component during this coarse treatment.
Another problem is that PLA is inclined to become crystalline, especially when heated or subjected to prolonged stress, which affects the surface properties and, in turn, the effectiveness of the bond. Additionally, bonded joints often have mechanical properties that are inferior to those of the original, unbonded material; hence, it is essential to consider the ultimate application of the mechanical characteristics required. Finally, regarding bonds, there may be additional concerns due to the presence of moisture in the air, as PLA laminates are expected to degrade in adhesive composite properties with sustained exposure to moisture. This creates the position that such challenges would require appropriate material preparation and proper application of adhesive on the said material as well as observing paintable weather conditions for the bond to be strong and long-lasting.
The Importance of Choosing the Right Glue for PLA
The right adhesive selection for joining PLA, durable and reliable forms is of utmost importance. The physical and chemical composition of PLA can be quite challenging, leading to the use of special-purpose adhesives bonds instead of conventional glues. For example, Cyanoacrylate (super glue) is one of the commonly used adhesives for PLA, but is not reflective of the stress or impact strength. On the contrary, with more extensive applications, flake adhesives are stronger and more resistant to weathering, albeit with longer curing periods. Such is the nature of flex connecting elements in holding piezo-electric vibrators on extreme temperatures.
Modern glue industry technologies have recently developed solvent-based and polyurethane adhesives formulated to work with thermoplastics. It should be emphasized that these new types are perfectly suited to the molecular structure of PLA. This is because the alternatives have been deliberately developed with the PLA material in mind, allowing them to bond to the plastic satisfactorily. In this respect, the bonding of these joints becomes more subdued, slightly dissolving the PLA surface as it is being treated. To add to this, advanced engineering adhesives containing methylsalicylate are proving to be useful, especially in tough bonding conditions, as these joints do not crack under thermal expansion/contraction. Therefore, the determining factor for the adhesion of the glue to PLA should be the mechanical load (stress), the environmental factors and the nature of usage.
Best Glue for PLA: A Comprehensive Review

These categories of applications help in selecting the most suitable adhesives for PLA as per the intended use. The better adhesives or selected technique optimizes the outcome with the given process.
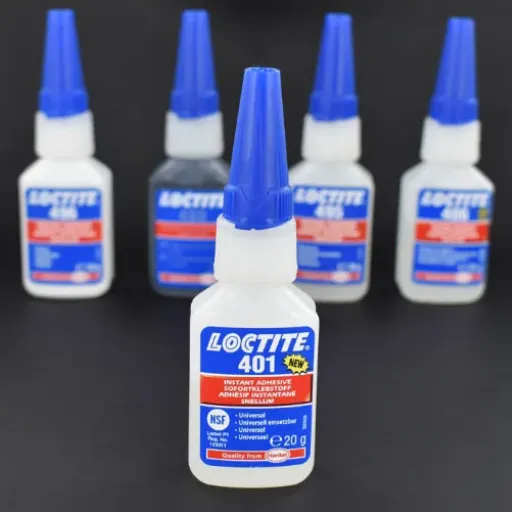
- Cyanoacrylate (Super Glue): 1This is one of the most popular choices for PLA due to its fast curing time and strong bond. It works well for small-scale repairs or models and is widely available.
- Epoxy Adhesives: A two-component adhesive is the most efficient for high-level adhesion that requires toughness or needs to endure bending. It is also effective when there are variations in temperature.
- Polyurethane Adhesives: Adhesives made from polyurethane are more advantageous in projects that require a bond that can withstand movement and resist high temperatures. These are also well suited in conditions comprising of low moisture or low levels of vibration.
- Methyl Methacrylate-Based Adhesives: Methyl methacrylate adhesives, such as LB-20, offer excellent strength and thermal resistance and are used in various machine-building structures as continuous elements.
When using any adhesive, it is essential to consider several factors, including joint size, exposure conditions, and the required service life. Prepare surfaces thoroughly for best results and maximal adhesion.
Top Adhesives for PLA Materials
To connect PLA parts, it is necessary to have a good adhesive that interacts properly with the material’s chemical structure. PLA is a biopolymer that is highly dependent on heat and has very limited chemical tolerance, making it complex to bond using certain chemicals. In the next section, the capabilities of the scientists will be shown as they have been practicing new breakthroughs:
- Cyanoacrylate Adhesives (Super Glue): Cyanoacrylate Adhesives used in small repairs, models, and crafts offer exceptional curing characteristics and quick bonding. These adhesives are likely compatible with PLA, with only superficial adhesion, in that they may crack in certain applications that require deformation.
- Epoxy Adhesives: For PLA, two-component preparations work particularly well as they provide excellent adhesion compared to other types of adhesives. Excellent specific bond strength and good thermal and moisture resistance allow easy adjustment of these specific adhesives.
- Hot Melt Adhesives: Melt adhesives also work well with PLA, as they form a remarkable adhesion with the substrate when applied to pure or rough PLA using a hot glue gun. They dry very fast and are excellent for prototype and non-structural applications.
- Polyurethane Adhesives: Offering flexibility above the average and added adhesiveness, polyurethane adhesives are the best choice for PLA applications where there is some level of stress or movement. They will withstand temperature changes as well.
- Plastic Weld Solvents: Even though these are not technically advanced adhesives, some aggressive plastic solvents do work on a particular adhesive under the right conditions. These solvents include products such as Dichloromethane or other suitable solvents for PLA; however, caution should be taken, as some are hazardous.
Comparing Glue Types for PLA
|
Glue Type |
Key Features |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Super Glue (CA) |
Fast-drying, strong bond |
Easy to use, widely available |
Brittle, limited gap-filling capabilities |
Small, rigid parts |
|
Epoxy |
Two-part adhesive, excellent strength |
High durability, gap filling, waterproof |
Longer curing time, may require mixing |
Large or structural components |
|
Hot Glue |
Thermoplastic polymer adhesive |
Quick setting, reusable with heat |
Weak at high temperatures, less durable |
Temporary or low-stress applications |
|
Plastic Weld Solvent |
Chemically bonds PLA, creates permanent weld |
Super strong, seamless bond |
Requires proper ventilation, hazardous |
High-stress joints requiring permanence |
|
Polyurethane Glue |
Expands to fill gaps, moisture-curing |
Strong bond, weather-resistant |
Can be messy, requires moisture to cure |
Complex joints or outdoor applications |
|
UV-Curing Adhesive |
Cures with UV light for precision |
High precision, clean application |
Requires UV light source, specific handling |
Transparent or delicate components |
|
PLA-Specific Glues |
Formulated specifically for PLA |
Optimized for PLA adhesion |
Limited availability, may be more expensive |
General PLA projects for convenience |
Practical Techniques for Bonding PLA

- Surface Preparation
It is recommended that after bending the adhered parts, they be thoroughly cleaned and sanded to improve the bonding. Use fine sandpaper to achieve light scratches over the surface; this will assist in holding the adhesive better.
- Adhesive Selection
Choose an adhesive suitable for PLA. These include cyanoacrylate adhesive, which allows the creation of rapid and substantial bonds, or which are specific to PLA. For cases where the product is more complex and will be subjected to external environments, it is best to use epoxy to achieve a longer bond life.
- Application Method
Spread a reasonable amount of adhesive over the primed surface using an appropriate spatula. Apply a measured amount of pressure enough to hold the parts in position when the adhesive is setting.
- Curing and Finishing
Follow the curing instructions of the bonded area scrupulously. As soon as it is cured, evaluate the amount of extra adhesive, make sure there are none and that there are no extra adhesives in sight for neat cut or visual parts.
Surface Preparation Tips for Optimal Adhesion
- Clean the Surface Thoroughly
The wetting layer provides a slippery surface that has relatively lower adhesive strengths. The use of more than 90% isopropyl alcohol has a strong cleaning effect on the surface. In addition, considering adhesion improvements, there are claims of 40% higher adhesion performance when edges are treated. Ensure that the surfaces are thoroughly cleaned and dry before proceeding.
- Roughen the Bonding Area
Speaking of bond strength, the smoothing of the PLA surface presents many inhibitions of mechanical adhesion. Use fine grit sandpaper, such as that between 220 and 400 grit, to rough the area to induce bonding by scratching it so that the adhesive can hold. This procedure can enhance bond strength by 25-50% with respect to the adhesive.
- Remove Residual Particles
After sanding the surfaces, the remnants are removed with the aid of the brush or by blowing compressed air over the surfaces. Occasionally, dust in conjunction with static charges developed on such dust can interfere with the better adhesion of extremely thin bonding films, irrespective of the type of bonding involved. This ensures that the surface upon which the adhesive will be fixed is not covered with any dust that can interfere with the adhesive’s efficiency.
- Dry and Pre-Warm the PLA Surface
PLA is known to be especially vulnerable to moisture and can absorb a very minimal amount, especially in conditions that are humid. Therefore, the use of a heat gun or warm hairdryer at low temperatures (e.g. 40- 50°C) can be used to pre-warm the surface gently. Such pre-warming will cause any moisture that is left on the surface after cleaning to evaporate and provide the most conducive condition for bonding. There is recorded data that demonstrates a 10–20% improvement in adhesion strength due to the pre-heating process.
- Apply a Primer if Necessary
For some adhesives, such as cyanoacrylate and, in one case, epoxy, primer application may be needed to boost adhesion values. If such enhanced performance is required, refer to the recommendations provided by the adhesive manufacturer. If adhesion on surfaces that cannot be treated is the primary problem, some changes may be made in the adhesive such as primer coating of the surfaces affected by the chemical reaction.
Application Techniques for a Clean Bond
- Ensure Proper Surface Cleaning
Any such entities like dirt, fats, or petroleum that might be on the bonded surfaces can be the main limiting factor in the effective use of an adhesive on a given joint. Clean the area first by a mix of isopropyl alcohol or any other solvent that is compatible with the created compound. This will ensure that all cleaning agents have been removed from cleaned areas before they are subjected to more procedures to prevent any moisture entrapment which can be detrimental to the bond.
- Use the Correct Amount of Adhesive
The use of excessive adhesive often leads to squeeze-out, making a messy and potentially weak bond. On the other hand, less adhesive can lead to incomplete adhesion resulting in decreased bond strength. указатели. обычно производитель дает рекомендации наилучших толщин приложения, рекомендуемых к исполнению напрямую на максимальную эффективность.
- Uniform Pressure Application
The same applies in case the adhesive has been deposited; apply a good, tight, and consistent pressure evenly around the bonded region. This aids in the proper application of the adhesive and prevents any gas pockets in the adhesive as well. There will be differences in the pressure applied and the amount of time taken based on the particular adhesive but using aids such as clamps or presses would definitely help in maintaining any uniformity during the curing phase.
- Maintain Appropriate Temperature and Humidity Levels
The two main factors that affect bonding quality are ambient temperature and relative humidity. Higher than normal temperatures decrease the amount of “waiting period” during which the adhesive is held for curing, and in case of dry (or very humid) weather, chemicals undergoing reaction of the adhesive might not react appropriately. For recommendations on the conditions of use and curing consult the product’s technical data sheet provided by the manufacturers.
- Allow Adequate Curing Time
The process of curing or hardening of an adhesive involves the adhesion bonding to the substrates and a waiting period in which the adhesive becomes sufficiently cured. Factors such as temperature, adhesive type, and the substance being bonded can affect the time it takes for a particular bond to cure. The bond may lose its integrity if stress is applied before the cure is complete. Therefore, ensure that the bond is allowed sufficient time to cure according to the recommendations provided in the technical data sheets.
Common Use Cases for PLA Glue

- 3D Printing Assembly
Polylactide (PLA) is a reversible plastic adhesive that is particularly useful for joining PLA parts made from PLA filament on account of the good bonding strength it provides for multipart projects.
- Prototyping and Model Repair
This adhesive is used to fill the hydrogel gaps, if any, between the prototype or model, modelling wood or other types of space filler, which are lightweight but due to their cross-section, they still give strength.
- Creative DIY Projects
PLA glue is often used in performing arts, crafts, or hobbies where the 3D printer’s PLA is mixed with other materials for occasional or decorative reasons.
- Educational and Hobbyist Projects
Students or amateurs instead use the pretty glue to assemble small-scale objects, which is easy to work with and pairs well with PLA.
Repairing 3D Printed Parts: Best Practices
- Evaluate the Damage
To begin, the broken section should be carefully examined to estimate the complexity of the damage, such as cracks, breaks, or loss of some parts. For minute cracks, bonding adhesives like cyanoacrylate or epoxy is good enough chemicals for solid adhesion. In the case of larger defects, reprinting the section or including other sections as a substitution may be more advisable.
- Prepare the Surface
The importance of prepping the surface is that fingerprints, blushes, and contamination can all be removed easily, and streaky primer can be avoided. If PLA or even an ABS part, the surface should be lightly sanded, which will change its texture, which is a necessary change to ensure proper bonding of glue and filler material. Expect that the digestive incarceration will be grafted successfully and that the repairs will last a long period. Or, make sure there is an even lip on the reparations.
- Choose the Right Adhesive or Repair Material
Supplement and adhesives or repair materials should be employed, accounting specifically for the filament inhibitors in use, e.g, PLA, ABS, PETG. While using PLA, there are specific adhesives that have been developed which are made to be used at lower temperatures, and these serve very well compared to the use of other traditional adhesives with practical adhesive ablation. This is very crucial for introduction besides ABS, since, in such cases, the joint can be welded using acetone such that it is completely submerged while no joints remain visible or accessible.
- Reinforce Structural Integrity
For high-stress areas or repairs of heavy components, additional reinforcement or embedding of material in the part may be carried out. For example, it would be beneficial to place steel rods inside a concrete beam or apply superimposed adhesive on several occasions. Stressing one of them is within the scope of adhesives. For more advanced bonding, thermal treatments are also available as a means of improving mechanical characteristics.
- Finish and Smooth
Once the repair of the affected area has been completed, do not forget to use fine-grit sandpaper to get rid of those visible seams or raised off surfaces. For cosmetic enhancement on the part use the fitting application which agrees with the model color paint and primer. Additional procedures, such as mechanical steps, vignetting, can improve the standard quality of the repair.
Assembling Complex Models with Adhesives
When assembling multi-part 3D objects that involve a complex structure, the type of adhesive used plays a crucial role in the final outcome, strength, and precision. In addition, bonding agents suitable for use with PLA materials are more flexible in terms of material bonding, whereas stress tends to compromise the strength of the material most often used. It will always come down to the choice of materials, whether the adhesive actually sticks to the plastic or not.
Troubleshooting PLA Adhesion Issues

- Bed Temperature Settings
It is essential to maintain the print bed temperature within the correct range, typically 55°C-70°C. If adhesion is still a concern, one might want to tweak the value within these limits(55-70) following the guidelines of the filament used.
- Surface Preparation
A clean and dust-free, well-bonded build plate is probably one of the most compelling instances for remedying adhesion failures. Preparing the build plate for printing involves cleaning with isopropyl alcohol to remove any visible marks from dust, grease or other debris. Lastly, offering improved adhesion may involve using a small amount of adhesive, such as a glue stick, painters’ tape, or a commercial adhesion sheet.
- Filament and Nozzle Calibration
Once the machine is ready, the next stage is to allow the nozzle. This will depend on the specific plastic used; however, for PLA printing, the nozzle temperature should be between 190°C and 220°C. Any other temperature than a suitable nozzle temperature can result in adhesion problems to the floor of the part in most cases.
- Bed Leveling
The symptom of the first undesirable effect could be the inadequacy of the first layer adhesion. Adjusting the print bed for uniform printing of each layer will help avoid rough areas, producing uneven surfaces or bad prints.
- Cooling Fan Settings
For the first few layers, cool the print by slowing the fan speed. This makes sure the material gets enough time to be adequately bonded before cooling starts.
Identifying Weak Bonds and Their Causes
The lack of cohesion in PLA (Polylactic Acid) hardly affects production volumes but rather can be attributed primarily to the specifics of surface preparation, processing conditions, use conditions, and adhesive preparation, among others. Cleaning of the surface is a major issue as well: the appearance of any impurities, such as dust, oil, or self-finish, has a great impact on the bonding quality of applied adhesives. Furthermore, the inapplicability of the adhesive without additional treatment is due to the properties of PLA itself, which do not allow the manufacturing process to be affected, thereby preventing the increase in adhesion area through micro-roughening the surface, as with latticing.
Environmental conditions, such as low temperatures and high humidity, can also create conditions in which adhesion is unable to last due to issues with curing time and changes in certain adhesive structural features. High ambient humidity can be a problem since humidity-sensitive adhesives may dry up before curing under normal circumstances. Furthermore, the formation of joints that do not hold under pressure can arise due to the use of improper adhesive formulations where the adhesive used does not contain the proportion of emulsion that would allow it to fill good joints between PLA and some other thermoplastics, like the adhesive designed by the previous character.
To detect these deficiencies precisely, various techniques such as pull tests and visual determination of the bond line are necessary to demarcate areas of low adhesion. These factors should be no more difficult to understand because they would enable the increase of “grain-bonding” and enhance the joint strength of any PLA work.
Dealing with Messy Applications
Mechanical and heat-induced stresses resulting from the polymerization shrinkage of the adhesive must be considered to control their impact on the strength and durability of the joints. This, in turn, can be emphasized by the fact that a bond in which the adhesive is only applied at strategic points (such as stress-sensitive corners) would have no more durability than a purely mechanical bond.
In adhering to the above advice, there still remains the case of application challenges that result from human error. Notably, high-precision application tools are available to address these challenges, including dispenser nozzles designed to deliver an accurate quantity of adhesive as one such method. Not to be forgotten, the added need to employ temperature control systems is essential, as these will help regulate the viscosity of the adhesive, ensuring it is spread evenly. In addition, adhesives can be ensured to be spread equally in the given field of interest by the use of automated systems with visual sensors. Only application in this manner, other than having a neat appearance, guarantees application evenness, reliability of adhesion, and the joint’s ultimate strength in the construction of the PLA base.
Reference Sources
1. The Studies on the Production of Polylactide’s Paper Adhesive: This study explored the development of biodegradable adhesives using polylactide (PLA) as the base material. Four adhesive formulations were tested, including PLA dissolved in chloroform with various additives like pigments, essential oils, and corn flour. The study concluded that PLA-based adhesives could be optimized for environmental safety and effective bonding.
2. Synthesis of Glues with Citric Acid and Sulfuric Acid Protonic Acid-H+ as Catalysts Using Banana Peel and Kaki as Valorized Raw Materials: This research focused on synthesizing eco-friendly glues using banana peel and kaki (persimmon) as raw materials. The sulfuric acid-based glue showed superior bonding due to its ability to catalyze dehydration and addition reactions, forming strong covalent bonds. The study highlighted the potential of using agricultural waste for adhesive production.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the best glue for PLA 3D printed parts?
A: The best glue for PLA 3D printed parts often includes options like super glue gel, gorilla glue, and Loctite. These adhesives bond PLA pieces together effectively, providing strong joints that can withstand stress. Additionally, using a gel control type of super glue can help you apply the glue in a more controlled manner, minimizing mess. It’s important to ensure that the surface of the PLA is clean before applying the adhesive for optimal results. For larger gaps, consider using a solvent-based glue like MEK, which can actually melt the PLA slightly to create a stronger bond. Always test the glue on a small area first to ensure compatibility with your PLA material.
Q: How do I glue PLA pieces together effectively?
A: To glue PLA pieces together effectively, start by selecting a suitable adhesive such as Loctite Ultra Gel or Gorilla Glue. Clean the surfaces of the pieces you want to bond to remove any dust or oils, which can interfere with adhesion. Apply the glue evenly and use clamps or weights to hold the pieces together while the adhesive cures for the best bond. Many super glues set quickly, typically within 15-30 seconds, which can be advantageous for quick repairs. For a more robust bond, consider using a mixture of model cement and an accelerator to speed up the curing process. Remember to work in a well-ventilated area, especially when using solvent-based adhesives.
Q: Can I use super glue for PLA?
A: Yes, you can use super glue for PLA, and it’s one of the most popular choices among hobbyists. Super glue, especially super glue gel, provides a strong bond that sets almost instantly, making it ideal for quick repairs or assembly. When applying the glue, ensure that you use just enough to cover the joint without leaving a gap, as this can weaken the bond. If you’re looking for a more flexible joint, you might want to explore using Gorilla Glue, which expands as it cures and can fill gaps. Keep in mind that super glue has a shelf life, so check the expiration date before using it on your projects. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the best results.
Q: What are the benefits of using gel control adhesives for PLA?
A: Gel control adhesives offer several benefits when working with PLA, particularly for precision applications. These adhesives allow for controlled application, reducing the risk of excess glue that could create unsightly messes or weaken the bond. Since they don’t run like liquid adhesives, they are perfect for vertical surfaces and intricate assemblies. Additionally, gel control adhesives typically cure quickly, which means your prints can be assembled and used sooner. Some brands even offer a dual-component system where an activator can be applied to speed up the curing process. Overall, gel control adhesives are an excellent choice for those looking for a tidy and efficient way to glue PLA parts together.
Q: Is there a specific glue for PLA 3D prints that is recommended?
A: When it comes to a specific glue for PLA 3D prints, many enthusiasts recommend using cyanoacrylate (CA) glue, commonly known as super glue. This adhesive is especially effective for joining small parts and creating strong glue joints. For larger surfaces or structural components, you might consider using Weld-On 16, which is designed for solvent bonding and can actually melt the PLA slightly for a stronger bond. Another option is using 3D Gloop, specifically formulated for bonding 3D printed parts, which fills gaps and creates a solid joint. Always evaluate the specific requirements of your project before choosing your adhesive, as some glues may work better than others depending on the application.



















